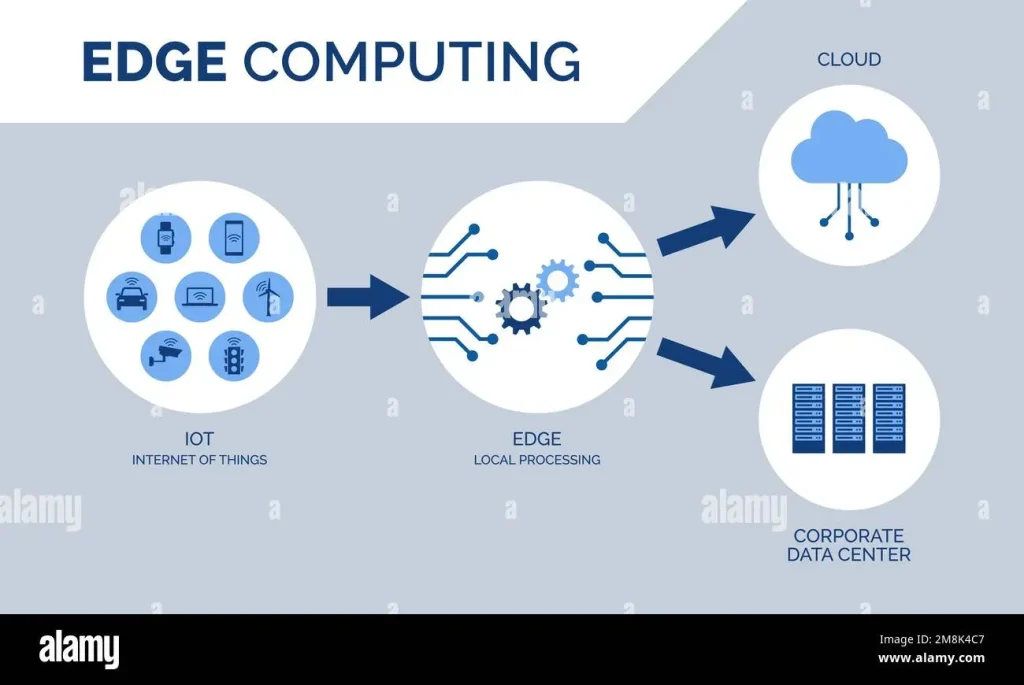
Edge Technology and IoT are reshaping how enterprises operate by bringing computation and decision-making closer to where data is produced. IoT edge devices deployed across factories, fleets, and facilities reduce latency and enable near-real-time actions. This model delivers edge computing benefits for enterprises by lowering bandwidth use, speeding insights, and increasing system resilience. Edge security for IoT becomes more achievable as data processing stays local and security controls are tightly enforced at the device and gateway level. The combined stack supports edge computing for enterprises and industrial IoT edge initiatives, unlocking new efficiencies and business models.
Viewed through an alternative lens, this approach is sometimes described as near-edge processing or fog computing, where computing moves close to devices rather than into distant clouds. Networks support distributed analytics at the network edge, enabling real-time monitoring and autonomous responses on the factory floor, in vehicles, and in remote sites. Adopting a hybrid edge-to-cloud strategy helps balance immediate local actions with deeper insights from centralized data stores, aligning with practical deployment in industrial automation projects.
Edge Technology and IoT: Real-Time Enterprise Intelligence
Edge Technology and IoT bring compute, storage, and analytics closer to where data is generated—from factory floors to remote facilities. For enterprises, this proximity reduces latency, lowers bandwidth costs, and enables immediate actions on sensor and device data. IoT edge devices, gateways, and local compute nodes work together to filter, analyze, and act before information ever leaves the site.
This edge-centric approach forms a multi-layer architecture that pairs edge computing for enterprises with centralized cloud analytics. By processing data locally, organizations improve response times for critical operations, maintain continuity during connectivity outages, and free bandwidth for strategic workloads. The result is a more resilient, scalable model that aligns with digital transformation goals.
Security and governance are embedded at the edge through edge security for IoT practices such as secure boot, hardware-based encryption, strict access controls, and regular firmware updates. When data stays closer to its origin, enterprises also strengthen compliance by limiting exposure and applying local privacy measures.
Industrial IoT Edge: Case-Driven Deployments, Security, and Resilience
Industrial IoT edge technologies empower manufacturing plants, refineries, and warehouses to monitor equipment health and production metrics with near-zero latency. By processing data on-site, edge computing for enterprises supports predictive maintenance, faster fault detection, and optimized throughput. IoT edge devices collect sensor streams and feed them to local analytics on gateways or edge servers, reducing data delays and enhancing operational visibility.
Deployment patterns in industrial settings emphasize reliability and security. Edge gateways can operate in hazardous environments, run fault-tolerant runtimes, and forward summarized results to the cloud for longer-term analysis. Emphasizing industrial IoT edge capabilities helps ensure regulatory compliance, data governance, and scalable growth across sites.
Security and resilience are not afterthoughts in industrial contexts. Edge security for IoT in these environments includes tamper-evident hardware, secure firmware updates, zero-trust access, and robust incident response. A practical ROI emerges from improved uptime, lower energy waste, and faster time-to-value as operations scale across facilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is edge computing for enterprises, and how does it improve IoT edge devices and real-time decision-making?
Edge computing for enterprises brings compute and analytics closer to where data is generated, enhancing IoT edge devices by enabling local processing, lower latency, reduced bandwidth, and faster, actionable insights. By processing data at the edge, organizations can realize edge computing benefits for enterprises such as improved responsiveness, resilience, and security, while still using cloud services for long-term storage and broader analytics in a hybrid edge-to-cloud architecture.
Why is edge security for IoT essential in industrial IoT edge deployments, and what practices help secure data at the edge?
Edge security for IoT is critical because data is processed and stored closer to the source in industrial environments, expanding the attack surface if not properly protected. Key practices include secure boot, hardware-based encryption, zero-trust access controls, regular firmware updates, robust device lifecycle management, and comprehensive data governance. A secure edge also relies on continuous monitoring, strong access controls, and an incident response plan to maintain safety and compliance.
| Section | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Introduction |
|
| What is Edge Technology and IoT? |
|
| Benefits and Business Outcomes |
|
| Key Components and Architecture |
|
| Industrial IoT Edge and Industrial Applications |
|
| Security, Privacy, and Compliance at the Edge |
|
| Operational Excellence: Deployment, Management, and ROI |
|
| Practical Deployment Best Practices |
|
| Case Studies and Industry Scenarios |
|
| Challenges and Pitfalls to Avoid |
|
| Future Directions: AI at the Edge and Beyond |
|
Summary
Edge Technology and IoT offer a practical framework for enterprises to become more responsive, efficient, and secure. By bringing compute and analytics closer to where data is produced, organizations can reap faster decision-making, reduced operating costs, and improved user experiences. The journey requires thoughtful planning, robust security, and a willingness to adopt hybrid architectures that balance edge and cloud capabilities. With a clear strategy, enterprises can unlock the full potential of edge computing and IoT, delivering tangible value across industries and geographies.